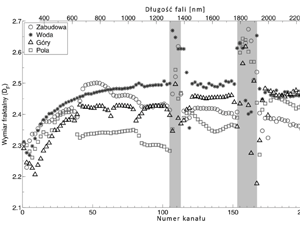
Wawrzaszek A., Walichnowska M., Krupiński M. (2015) Evaluation of degree of multifractality for description of high resolution data aquired by Landsat Satellites, Archiwum Fotogrametrii, Kartografii i Teledetekcji 2015, vol. 27, s. 175-184 ISSN 2083-2214, eISSN 2391-9477, doi:10.14681/afkit.2015.013
In the frame of this work six satellite images (at six spectral bands) from Landsat 5, Landsat 7 and Landsat 8 have been analysed. For this purpose 30 meter resolution images showing the regions
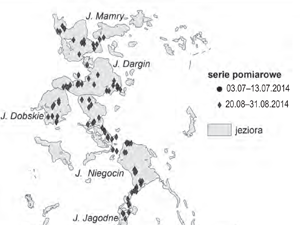
Kulczyk S.,Woźniak E. , Derek M. , Kowalczyk M. (2015) Pomiar marszrutowy jako narzędzie monitoringu aktywności turystycznej. Przykład Wielkich Jezior Mazurskich. Problemy Ekologii Krajobrazu, T. XXXIX, 111–119
In order to describe relations between tourism and landscape, it is important to operate within two scopes. The first is landscape potential and the second – the way it is used by tourists. In
Nowakowski A. (2015) Remote Sensing Data Binary Classification Using Boosting with Simple Classifiers, Acta Geophys. (2015) 63: 1447, doi: 10.1515/acgeo-2015-004
Boosting is a classification method which has been proven useful in non-satellite image processing while it is still new to satellite remote sensing. It is a meta-algorithm, which builds a strong classifier from many
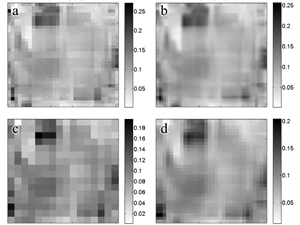
Wawrzaszek A., Krupiński M., Drzewiecki W., Aleksandrowicz S. (2015) Multifractal analysis of satellite images, Archiwum Fotogrametrii, Kartografii i Teledetekcji 2015, vol. 27, s. 163-173 ISSN 2083-2214, eISSN 2391-947, doi: 10.14681/afkit.2015.012
Research presented in this paper is focused on the efficiency assessment of multifractal description as a tool for Image Information Mining. Large datasets of very high spatial resolution satellite images (WorldView-2 and EROS-A) have
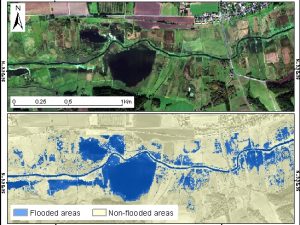
Malinowski R., Groom G., Schwanghart W., Heckrath G. (2015) Detection and delineation of localized flooding from worldview-2 multispectral data. Remote Sensing 2015, 7, 14853-14875, doi: 10.3390/rs71114853
Remote sensing technology serves as a powerful tool for analyzing geospatial characteristics of flood inundation events at various scales. However, the performance of remote sensing methods depends heavily on the flood characteristics and landscape
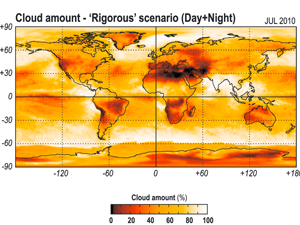
Kotarba, A.Z. (2015) Impact of Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) cloud mask interpretation on cloud amount estimation, Journal of Geophysical Research, Volume 120, Issue 17, September 2015 Pages 8971–8986, doi: 10.1002/2015JD023277
Cloud masks serve as a basis for estimates of cloud amount, which is an essential parameter for studying the Earth’s radiation budget. The most commonly used cloud mask is a simple thematic classification, which
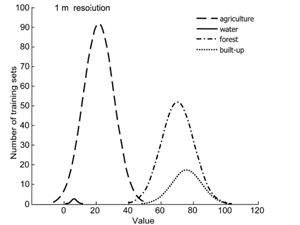
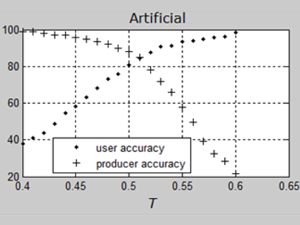
Lewiński S., Aleksandrowicz S., Banaszkiewicz M. (2015) Testing Texture of VHR Panchromatic Data as a Feature of Land Cover Classification, Acta Geophysica, Volume 63, Issue 2, pp 547–567, doi: 10.2478/s11600-014-0250-5
While it is well-known that texture can be used to classify very high resolution (VHR) data, the limits of its applicability have not been unequivocally specified. This study examines whether it is possible to

Malinowski, R.; Groom, G.; Schwanghart, W.; Heckrath, G. Detection and delineation of localized flooding from worldview-2 multispectral data. Remote Sensing 2015, 7, 14853-14875.
Remote sensing technology serves as a powerful tool for analyzing geospatial characteristics of flood inundation events at various scales. However, the performance of remote sensing methods depends heavily on the flood characteristics and landscape
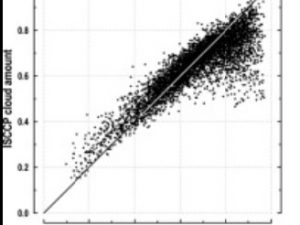
Kotarba A.Z. (2015) Evaluation of ISCCP cloud amount with MODIS observations, Atmospheric Research, vol. 153, 310-317, doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2014.09.006
The goal of the International Satellite Cloud Climatology Project (ISCCP) is to provide global cloud amount statistics for atmospheric radiation flux modeling, which is a key element of climate change studies. However, ISCCP estimates
 English version
English version