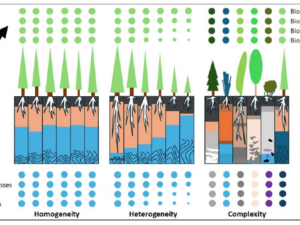
Beierkuhnlein C. (2025) et al. Towards a comprehensive geodiversity – biodiversity nexus in terrestrial ecosystems
The study address the need for an integrated approach to managing complex natural systems by linking geodiversity and biodiversity. These elements interact across scales, influencing climate and human land use while underpinning ecosystem services.

Sobczak-Szelc K. (2024) et al. Navigating environmental fragility: (Mal)coping and adaptation strategies in the socio-environmental system of the Mtendeli Refugee Camp, Tanzania
The study conducts a systems analysis of coping and adaptation strategies in Tanzanian refugee camps, focusing on the Mtendeli camp as a case study. It explores the environmental changes during the stages of the

Bałazy K. et al. (2024) Illuminating the Arctic: Unveiling seabird responses to artificial light during polar darkness through citizen science and remote sensing
Artificial light at night (ALAN) has global impacts on animals, often negative, yet its effects in polar regions remains largely underexplored. These regions experience prolonged darkness during the polar night, while human activity and
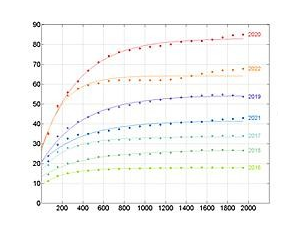
Domingo-Marimon C. et al. (2024) Developing an early warning land degradation indicator based on geostatistical analysis of Ecosystem Functional Types dynamics
Identifying and quantifying ecosystem degradation and recovery is of critical importance for ecosystem health, biodiversity, food security and the livelihoods of local communities. Remote sensing datasets and techniques, particularly land cover maps, provide crucial
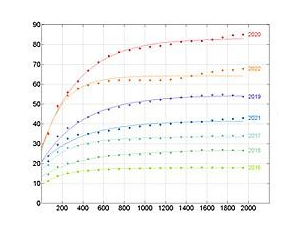
Domingo-Marimon C. et al. (2024) Developing an early warning land degradation indicator based on geostatistical analysis of Ecosystem Functional Types dynamics
Identifying and quantifying ecosystem degradation and recovery is of critical importance for ecosystem health, biodiversity, food security and the livelihoods of local communities. Remote sensing datasets and techniques, particularly land cover maps, provide crucial
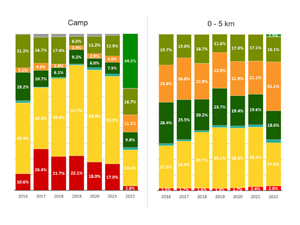
Gromny E. at al., (2024) Remote sensing insights into land cover dynamics and socio-economic Drivers: The case of Mtendeli refugee camp, Tanzania (2016–2022)
The purpose of this article is to present the scope and the dynamics of the environmental changes unfolded in the vicinity of Mtendeli refugee camp. It presents a new method, which combines geospatial analysis

SATMIROL
SATMIROL project aims to solve the problems faced by agricultural statistics and recipients of agricultural statistics by: development of methods based on satellite data from the European COPERNICUS program for: the identification and monitoring

Remote sensing as a recipe for effective urban adaptation to the effects of climate change
The ambition of the project ‘Using remote sensing to manage blue-green urban infrastructure for climate change adaptation’ (LIFECOOLCITY) is to support the management of blue-green infrastructure (BZI) in 10,000 cities in the European Union,

IntSen2
The basic assumption of the project is the use of artificial intelligence (AI) for fully automatic detection of military objects such as aircraft and boat. IntSen2 aims to support the operational autonomy of the
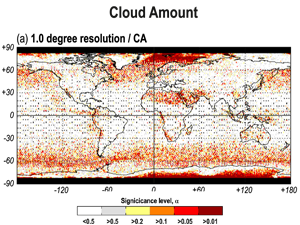
Kotarba, A.Z. (2022) Errors in global cloud climatology due to transect sampling with the CALIPSO satellite lidar mission
Although cloud profiling lidars provide the most accurate data on cloud amount (CA), cloud top height (CTH) and cloud optical thickness (COT), they only sample cloud fields along a one-dimensional transect. This approach introduces
 Wersja polska
Wersja polska English version
English version