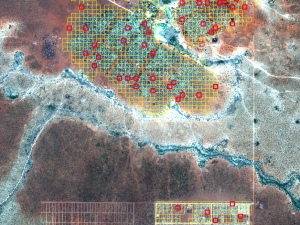
Jenerowicz M., Kemper T. (2016) An improved automated procedure for informal and temporary dwellings detection and enumeration, using mathematical morphology operators on VHR satellite data, Remote Sensing Technologies and Applications in Urban Environments, doi: 10.1117/12.2254808
Every year thousands of people are displaced by conflicts or natural disasters and often gather in large camps. Knowing how many people have been gathered is crucial for an efficient relief operation. However, it

S2GLC
At the beginning of February 2016 our group has started a new ESA project in the framework of Scientific Exploitation of Operational Missions (SEOM) S2-4Sci Land and Water. S2GLC is an international project implemented

ArtISS
ArtISS (Artificial Impervious Surfaces detection with Snow-featured satellite imagery) was a study to improve detection of artificial impervious surfaces using satellite images acquired during winter or night. Artificial impervious surfaces are the example of
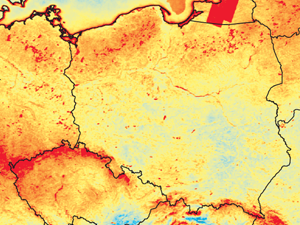
Kotarba A.Z. (2016) Regional high-resolution cloud climatology based on MODIS cloud detection data, Volume 36, Issue 8 30 June 2016 Pages 3105–3115, doi: 10.1002/joc.4539
Most satellite cloud climatologies come in the form of global, low-resolution datasets: so- called ‘gridded’ Level 3 products, resulting from the reprojection and spatio-temporal aggregation of swath (Level 2) data. Their coarse resolution means
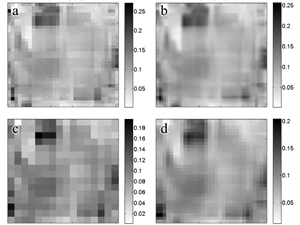
Wawrzaszek A., Walichnowska M., Krupiński M. (2015) Evaluation of degree of multifractality for description of high resolution data aquired by Landsat Satellites, Archiwum Fotogrametrii, Kartografii i Teledetekcji 2015, vol. 27, s. 175-184 ISSN 2083-2214, eISSN 2391-9477, doi:10.14681/afkit.2015.013
In the frame of this work six satellite images (at six spectral bands) from Landsat 5, Landsat 7 and Landsat 8 have been analysed. For this purpose 30 meter resolution images showing the regions
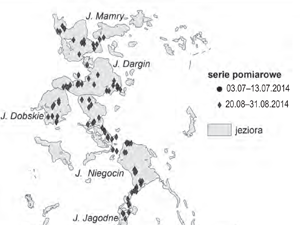
Kulczyk S.,Woźniak E. , Derek M. , Kowalczyk M. (2015) Pomiar marszrutowy jako narzędzie monitoringu aktywności turystycznej. Przykład Wielkich Jezior Mazurskich. Problemy Ekologii Krajobrazu, T. XXXIX, 111–119
In order to describe relations between tourism and landscape, it is important to operate within two scopes. The first is landscape potential and the second – the way it is used by tourists. In
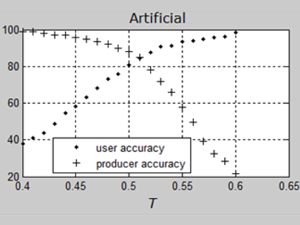
Nowakowski A. (2015) Remote Sensing Data Binary Classification Using Boosting with Simple Classifiers, Acta Geophys. (2015) 63: 1447, doi: 10.1515/acgeo-2015-004
Boosting is a classification method which has been proven useful in non-satellite image processing while it is still new to satellite remote sensing. It is a meta-algorithm, which builds a strong classifier from many
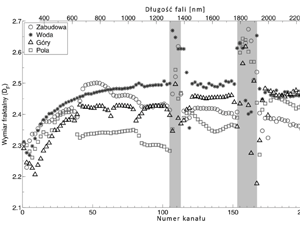
Wawrzaszek A., Krupiński M., Drzewiecki W., Aleksandrowicz S. (2015) Multifractal analysis of satellite images, Archiwum Fotogrametrii, Kartografii i Teledetekcji 2015, vol. 27, s. 163-173 ISSN 2083-2214, eISSN 2391-947, doi: 10.14681/afkit.2015.012
Research presented in this paper is focused on the efficiency assessment of multifractal description as a tool for Image Information Mining. Large datasets of very high spatial resolution satellite images (WorldView-2 and EROS-A) have
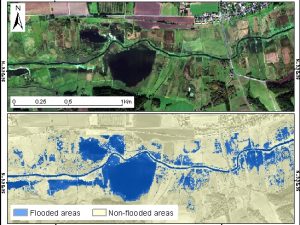
Malinowski R., Groom G., Schwanghart W., Heckrath G. (2015) Detection and delineation of localized flooding from worldview-2 multispectral data. Remote Sensing 2015, 7, 14853-14875, doi: 10.3390/rs71114853
Remote sensing technology serves as a powerful tool for analyzing geospatial characteristics of flood inundation events at various scales. However, the performance of remote sensing methods depends heavily on the flood characteristics and landscape
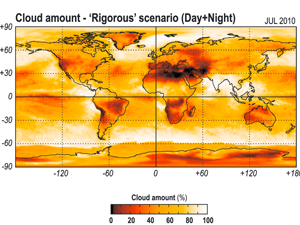
Kotarba, A.Z. (2015) Impact of Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) cloud mask interpretation on cloud amount estimation, Journal of Geophysical Research, Volume 120, Issue 17, September 2015 Pages 8971–8986, doi: 10.1002/2015JD023277
Cloud masks serve as a basis for estimates of cloud amount, which is an essential parameter for studying the Earth’s radiation budget. The most commonly used cloud mask is a simple thematic classification, which
 Wersja polska
Wersja polska English version
English version