
Beierkuhnlein C. (2025) et al. Towards a comprehensive geodiversity – biodiversity nexus in terrestrial ecosystems
The study address the need for an integrated approach to managing complex natural systems by linking geodiversity and biodiversity. These elements interact across scales, influencing climate and human land use while underpinning ecosystem services.
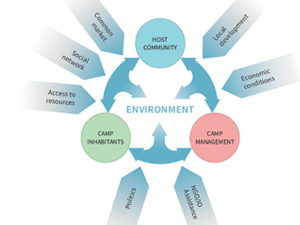
Sobczak-Szelc K. (2024) et al. Navigating environmental fragility: (Mal)coping and adaptation strategies in the socio-environmental system of the Mtendeli Refugee Camp, Tanzania
The study conducts a systems analysis of coping and adaptation strategies in Tanzanian refugee camps, focusing on the Mtendeli camp as a case study. It explores the environmental changes during the stages of the

Bałazy K. et al. (2024) Illuminating the Arctic: Unveiling seabird responses to artificial light during polar darkness through citizen science and remote sensing
Artificial light at night (ALAN) has global impacts on animals, often negative, yet its effects in polar regions remains largely underexplored. These regions experience prolonged darkness during the polar night, while human activity and
Wojciechowska, I., Kotarba, A. Z., & Żmudzka, E. (2023). Cloud type frequency over Poland (2003–2021) revealed by independent satellite-based (MODIS) and surface-based (SYNOP) observations
Recent studies have identified several statistically significant trends in cloud genera frequency over Poland. Notably, there has been an increase in high and convective clouds, along with a decrease in Stratus, Altostratus and Nimbostratus.
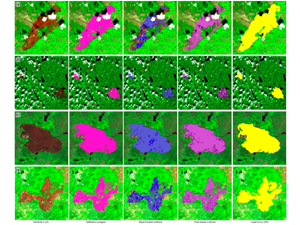
Milczarek, M., at al (2023). Object- Versus Pixel-Based Unsupervised Fire Burn Scar Mapping under Different Biogeographical Conditions in Europe
Wildfire detection and mapping is crucial for managing natural resources and preventingfurther environmental damage. In this study, we compared two methods of mapping burn scarsusing Sentinel-2 satellite imagery, a pixel-based approach and an object-based
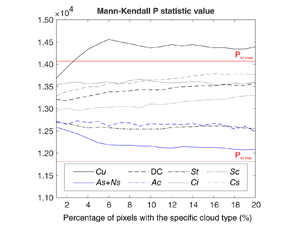
Kotarba, A.Z. (2022) Errors in global cloud climatology due to transect sampling with the CALIPSO satellite lidar mission
Although cloud profiling lidars provide the most accurate data on cloud amount (CA), cloud top height (CTH) and cloud optical thickness (COT), they only sample cloud fields along a one-dimensional transect. This approach introduces
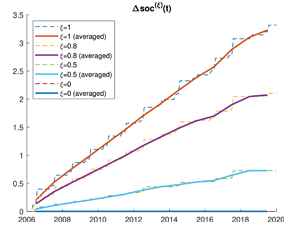
Diele F., Luiso I., Marangi C., Martiradonna A., Woźniak E. (2022) Evaluating the impact of increasing temperatures on changes in Soil Organic Carbon stocks: sensitivity analysis and non-standard discrete approximation
The SOC change index, defined as the normalized difference between the actual Soil Organic Carbon and the value assumed at an initial reference year, is here tailored to the RothC carbon model dynamics. It
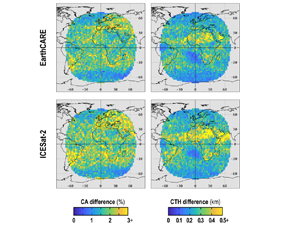
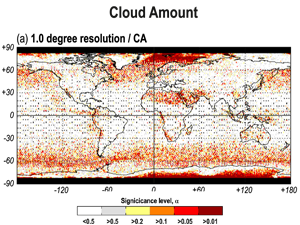
Kotarba, A. Z. (2022) Impact of the revisit frequency on cloud climatology for CALIPSO, EarthCARE, Aeolus, and ICESat-2 satellite lidar missions
Space profiling lidars offer a unique insight into cloud properties in Earth’s atmosphere and are considered the most reliable source of total (column-integrated) cloud amount (CA), and true (geometrical) cloud top height (CTH). However,

Kotarba, A.Z, Nguyen Huu, Ż. (2022) Accuracy of cirrus detection by surface-based human observers
The longest cirrus time series are ground-based, visual observations captured by human observers [synoptic observations (SYNOP)]. However, their reliability is impacted by an unfavorable viewing geometry (cloud overlap) and misclassification due to low cloud
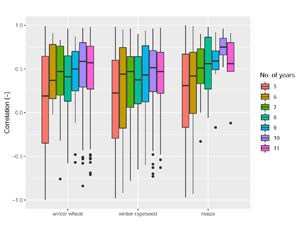
Bojanowski J., Sikora S., Musiał J., Woźniak E., Katarzyna Dąbrowska-Zielińska K., Slesiński P., Milewski T., Łączyński A. (2022), Integration of Sentinel-3 and MODIS Vegetation Indices with ERA-5 Agro-meteorological Indicators for Operational Crop Yield Forecasting
Timely crop yield forecasts at national level are substantial to support food policies, to assess agricultural production and to subsidize regions affected by food shortage. This study presents an operational crop yield forecasting system
 Wersja polska
Wersja polska English version
English version