
SATMIROL
SATMIROL project aims to solve the problems faced by agricultural statistics and recipients of agricultural statistics by: development of methods based on satellite data from the European COPERNICUS program for: the identification and monitoring

ACCESS-4FI
ACCESS-4FI – Automated Crop Classification and yield Estimation online ServiceS for Food Industry. This project addresses the challenge of quantification and annual monitoring of the agricultural production, as seen from the perspective of different

BAMS-Mazovia
The main goal of the BAMS-Mazovia (Build-up Areas Monitoring Service for Mazovia) project is to develop a service platform that would provide reliable information on changes occuring within built-up areas. The service will be

Jenerowicz M., Banaszkiewicz M. (2018), Asteroid (21) Lutetia: Semi-Automatic Impact Craters Detection and Classification. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens., doi:10.5194/isprs-archives-XLII-2-479-2018
The need to develop an automated method, independent of lighting and surface conditions, for the identification and measurement of impact craters, as well as the creation of a reliable and efficient tool, has become

Woźniak E., Kofman W., Lewiński S., Wajer P., Rybicki M., Aleksandrowicz S., Włodarkiewicz A. (2018), Multi-temporal polarimetry in land-cover classification. International Journal of Remote Sensing, doi:10.1080/01431161.2018.1483084
This study uses time-series Sentinel-1(S-1) synthetic aperture radar images to evaluate the impact of multi-temporal polarimetric processing on land-cover classification. Various polarimetric processing methods are applied to multi-temporal S-1 data set in order to

Kotarba A.Z., Nowakowski A. (2018), Impact of snow cover on impervious surface detection. International Journal of Remote Sensing, doi:10.1080/01431161.2018.1475775
Traditionally, snow cover has been seen as an obstacle to landcover classification and impervious surface detection based on remote sensing. However, snow cover increases the spectral contrast between impermeable surfaces and other land-use types.
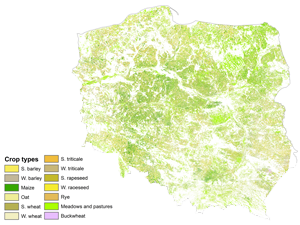
EOStat
EOStat – Services for Earth Observation-based statistical information for agriculture The project aims to develop methods for a collection of statistical information about agricultural production and methods for a control of farmers’ activity in
Kotarba A.Z., Vertical profile of cloud amount over Poland: variability and uncertainty based on CloudSat-CALIPSO observations. International Journal of Climatology, doi:10.1002/joc.5558
Historically, climatologists have found it difficult to access reliable information on cloud vertical structure. This is becaus e both surface-based observers and imaging/sounding satellite sensors have limited capability to report superposed cloud. How-ever, lidar–radar
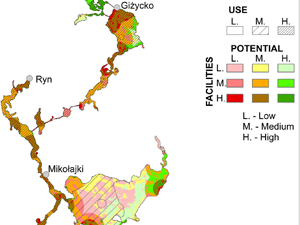
Kulczyk S., Woźniak, E., Derek, M. (2018) Landscape, facilities and visitors: An integrated model of recreational ecosystem services, Ecosystem Services, doi: 10.1016/j.ecoser.2018.02.016
Recreation is a complex and important ecosystem service. Therefore, there is a need for approaches that can account for this complexity, and integrate both environmental and socio-economical perspectives. The Recreational Ecosystem Services (RES) model

Woźniak E., Kulczyk S., Derek M. (2018) From intrinsic to service potential: An approach to assess tourism landscape potential, Landscape and Urban Planning, 170, 209-220, doi: 10.1016/j.landurbplan.2017.10.006
Tourism contributes to human well-being and is recognized as a cultural ecosystem service. However, assessments of landscape potential for tourism tend to be very general. Therefore, this study proposes a method that takes into
 Wersja polska
Wersja polska English version
English version