
Jenerowicz M., Wawrzaszek A., Krupiński M., Drzewiecki W., Aleksandrowicz S. (2019), Aplicability of Multifractal Features as Descriptors of the Complex Terrain Situation in IDP/Refugee Camps, IGARSS 2019
This paper presents the preliminary results of the complex terrain situation description with the utility of multifractal features. The analysis was done for two samples of Internally Displaced Person/Refugee camps (Ifo, Daadab in Kenya/Al
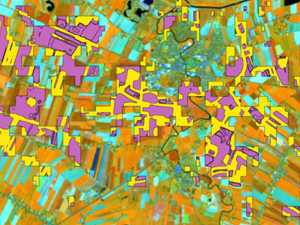
Gromny E., Lewiński S., Rybicki M., Malinowski R., Krupiński M., Nowakowski A., and Jenerowicz M. (2019), Creation of training dataset for Sentinel-2 land cover classification, Proc. SPIE
Supervised classification of satellite images is performed based on utilization of reference training data. Therefore, the availability and quality of reference data highly influences the results and the course of the entire classification process.
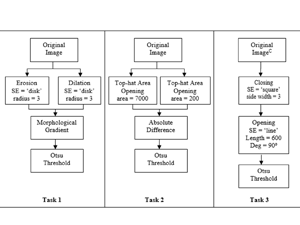
Jenerowicz M., Wawrzaszek A., Krupiński M., Aleksandrowicz S., and Drzewiecki W. (2019), Comparison of mathematical morphology with the local multifractal description applied to the image samples processing, Proc. SPIE
This paper presents the results of a preliminary comparison of two methods which are based on the mathematical approach, Mathematical Morphology and the Local Multifractal Description. Both methods are characterized by the need for
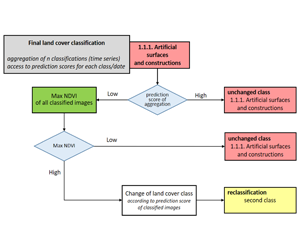
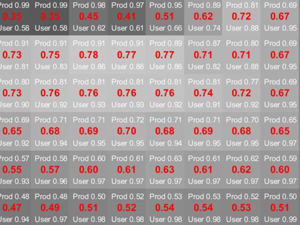
Gromny E., Lewiński S., Rybicki M., Malinowski R., Krupiński M., and Nowakowski A. (2019), Post-processing tools for land cover classification of Sentinel-2, Proc. SPIE
Post-processing is the last and often optional stage of land cover (LC) classification from satellite images. In the traditional approach, it is usually applied to remove the effect of “salt and pepper” from the
Krupiński M., Lewiński S., Malinowski R. (2019), One class SVM for building detection on Sentinel-2 images, Proc. SPIE
Human population has reached 7.7 billion in year 2019. According to the forecasts of world population projections it may reach 8 billion in 2023. This growth indicates inter alia increased demand for housing. Monitoring
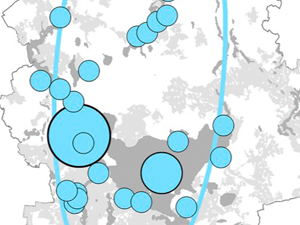
Derek M., Woźniak E., Kulczyk S. (2019), Clustering nature-based tourists by activity. Social, economic and spatial dimensions, Tourism Management
This study develops a typology of tourists visiting a nature-based destination as a function of outdoor activities. It then identifies social, economic and spatial differences between them. A cluster analysis is applied to survey
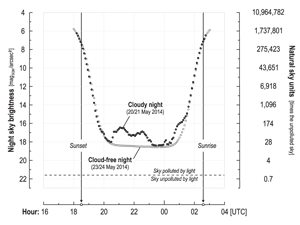
Kotarba A. Z., Chacewicz S., Żmudzka E. (2019), Night sky photometry over Warsaw (Poland) evaluated simultaneously with surface-based and satellite-based cloud observations, Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy & Radiative Transfer
Light pollution is a widely distributed form of anthropogenic pollution that threatens both biodiversity and human health. One of the most popular indicators is known as night sky brightness (NSB), mea- sured with photometric

Jenerowicz M., Banaszkiewicz M. (2018), Asteroid (21) Lutetia: Semi-Automatic Impact Craters Detection and Classification. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens., doi:10.5194/isprs-archives-XLII-2-479-2018
The need to develop an automated method, independent of lighting and surface conditions, for the identification and measurement of impact craters, as well as the creation of a reliable and efficient tool, has become

Woźniak E., Kofman W., Lewiński S., Wajer P., Rybicki M., Aleksandrowicz S., Włodarkiewicz A. (2018), Multi-temporal polarimetry in land-cover classification. International Journal of Remote Sensing, doi:10.1080/01431161.2018.1483084
This study uses time-series Sentinel-1(S-1) synthetic aperture radar images to evaluate the impact of multi-temporal polarimetric processing on land-cover classification. Various polarimetric processing methods are applied to multi-temporal S-1 data set in order to

Kotarba A.Z., Nowakowski A. (2018), Impact of snow cover on impervious surface detection. International Journal of Remote Sensing, doi:10.1080/01431161.2018.1475775
Traditionally, snow cover has been seen as an obstacle to landcover classification and impervious surface detection based on remote sensing. However, snow cover increases the spectral contrast between impermeable surfaces and other land-use types.
 Wersja polska
Wersja polska English version
English version