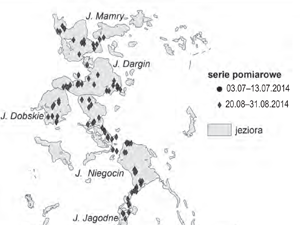
Kulczyk S.,Woźniak E. , Derek M. , Kowalczyk M. (2015) Pomiar marszrutowy jako narzędzie monitoringu aktywności turystycznej. Przykład Wielkich Jezior Mazurskich. Problemy Ekologii Krajobrazu, T. XXXIX, 111–119
In order to describe relations between tourism and landscape, it is important to operate within two scopes. The first is landscape potential and the second – the way it is used by tourists. In
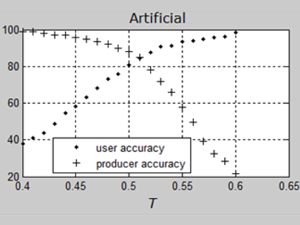
Nowakowski A. (2015) Remote Sensing Data Binary Classification Using Boosting with Simple Classifiers, Acta Geophys. (2015) 63: 1447, doi: 10.1515/acgeo-2015-004
Boosting is a classification method which has been proven useful in non-satellite image processing while it is still new to satellite remote sensing. It is a meta-algorithm, which builds a strong classifier from many
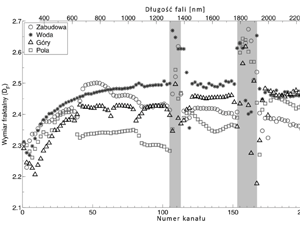
Wawrzaszek A., Krupiński M., Drzewiecki W., Aleksandrowicz S. (2015) Multifraktalna analiza zobrazowań satelitarnych , Archiwum Fotogrametrii, Kartografii i Teledetekcji 2015, vol. 27, s. 163-173 ISSN 2083-2214, eISSN 2391-947, doi: 10.14681/afkit.2015.012
Przedstawione prace badawcze dotyczyły oceny skuteczności stosowania opisu multifraktalnego jako narzędzia do wydobywania informacji z bardzo wysokorozdzielczych zobrazowań satelitarnych, prezentujących głównie obszary Polski. Przeanalizowano duże zestawy danych panchromatycznych, zarejestrowanych przez satelity WorldView-2 i EROS-A.
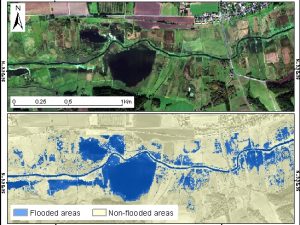
Malinowski R., Groom G., Schwanghart W., Heckrath G. (2015) Detection and delineation of localized flooding from worldview-2 multispectral data. Remote Sensing 2015, 7, 14853-14875, doi: 10.3390/rs71114853
Remote sensing technology serves as a powerful tool for analyzing geospatial characteristics of flood inundation events at various scales. However, the performance of remote sensing methods depends heavily on the flood characteristics and landscape
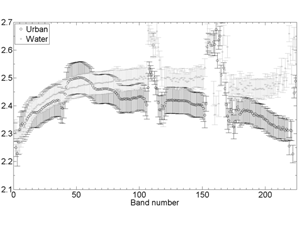
Krupiński M., Wawrzaszek A., Drzewiecki W., Aleksandrowicz S. (2014) Usefulness of the fractal dimension in the context of hyperspectral data description, SGEM2014 Conference Proceedings, ISBN 978-619-7105-12-4 / ISSN 1314-2704, June 19-25, 2014, Book 2, Vol. 3, 367-374 pp
The number of hyperspectral sensors and data grows systematically and dynamically. Hyperspectral data delivers huge number of precise information but character of data requires specific methods of processing. One of these methods can be

Drzewiecki W., Jenerowicz M., Aleksandrowicz S., Krupiński M. Spatial Modeling of Potential Ways of Crossing the Borders by Illegal Immigrants. Annals of Geomatics 2012, t.10 z4, pp 49-64
One of the main objectives of geographical information systems is to support the process of decision making. Spatial modeling can be a useful tool to provide such support also for the analyses of general

Krupiński M., Drzewiecki W., Wawrzaszek A., Aleksandrowicz S. Initial Evaluation of the Applicability of Multifractal Measures as Global Content-Based Image Descriptors. ESA-EUSC-JRC 8th conference on image information mining; 10/2013
Increasing amount of Very High Resolution (VHR) data requires new methods of information mining. In this paper we describe applicability of multifractal theory for VHR panchromatic image analysis. The aim of the study was

Testing Texture of VHR Panchromatic Data as a Feature of Land Cover Classification
While it is well-known that texture can be used to classify very high resolution (VHR) data, the limits of its applicability have not been unequivocally specified. This study examines whether it is possible to
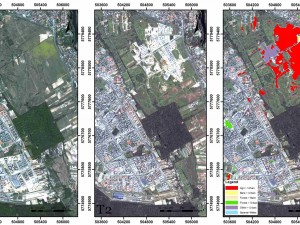
Change Detection Algorithm for the Production of Land Cover Change Maps over the European Union Countries
Contemporary satellite Earth Observation systems provide growing amounts of very high spatial resolution data that can be used in various applications. An increasing number of sensors make it possible to monitor selected areas in
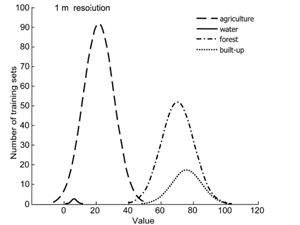
Lewiński S., Aleksandrowicz S., Banaszkiewicz M. (2015) Testing Texture of VHR Panchromatic Data as a Feature of Land Cover Classification, Acta Geophysica, Volume 63, Issue 2, pp 547–567, doi: 10.2478/s11600-014-0250-5
While it is well-known that texture can be used to classify very high resolution (VHR) data, the limits of its applicability have not been unequivocally specified. This study examines whether it is possible to
 Wersja polska
Wersja polska English version
English version