Kotarba A.Z. (2018) Vertical profile of cloud amount over Poland: variability and uncertainty based on CloudSat-CALIPSO observations. International Journal of Climatology, doi:10.1002/joc.5558
Historically, climatologists have found it difficult to access reliable information on cloud vertical structure. This is becaus e both surface-based observers and imaging/sounding satellite sensors have limited capability to report superposed cloud. How-ever, lidar–radar
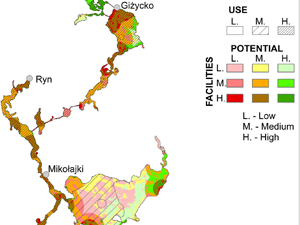
Kulczyk S., Woźniak, E., Derek, M. (2018) Landscape, facilities and visitors: An integrated model of recreational ecosystem services, Ecosystem Services, doi: 10.1016/j.ecoser.2018.02.016
Recreation is a complex and important ecosystem service. Therefore, there is a need for approaches that can account for this complexity, and integrate both environmental and socio-economical perspectives. The Recreational Ecosystem Services (RES) model

Woźniak E., Kulczyk S., Derek M. (2018) From intrinsic to service potential: An approach to assess tourism landscape potential, Landscape and Urban Planning, 170, 209-220, doi: 10.1016/j.landurbplan.2017.10.006
Tourism contributes to human well-being and is recognized as a cultural ecosystem service. However, assessments of landscape potential for tourism tend to be very general. Therefore, this study proposes a method that takes into
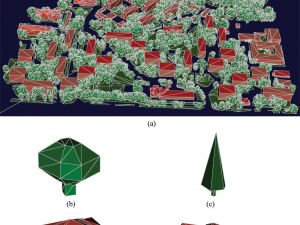
Wajer P., Woźniak E., Kofman W., Rybicki M., Lewiński S. (2018) Simulation of SAR images of urban areas by using the ray tracing method with measured values of backscatter coefficients, International Journal of Remote Sensing, 39:9, 2671-2689, doi: 10.1080/01431161.2018.1430396
This study uses the ray tracing method to simulate synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images of urban areas. The images are constructed for polarisations: horizontal-horizontal (HH) and vertical-vertical (VV), and different types of buildings, vegetation,

Kukawska E. et al. (2017) Multitemporal Sentinel-2 data – remarks and observations. 9th International Workshop on the Analysis of Multitemporal Remote Sensing Images (MultiTemp), Brugge, 2017, pp. 1-4, doi: 10.1109/Multi-Temp.2017.8035212
All the pre-processing algorithms are being improved constantly. The biggest challenge for the multitemporal analysis is to deal with errors caused directly by the chain of pre-processing of raw Sentinel-2 data to the level
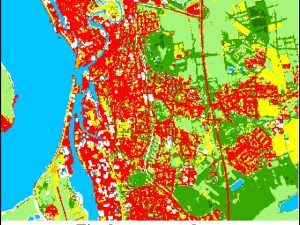
Lewiński S., Nowakowski A., Malinowski R., Rybicki M., Kukawska E., Krupiński M. (2017) Aggregation of Sentinel-2 time series classifications as a solution for multitemporal analysis. In Proc. SPIE 10427, Image and Signal Processing for Remote Sensing XXIII, 104270B doi: 10.1117/12.2277976
The general aim of this work was to elaborate efficient and reliable aggregation method that could be used for creating a land cover map at a global scale from multitemporal satellite imagery. The study
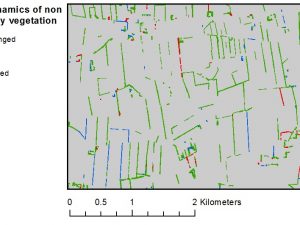
Angelidis I., Levin G., Díaz-Varela R. A., Malinowski R. (2017) Assessment of changes in formations of non-forest woody vegetation in southern Denmark based on airborne LiDAR. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 189(9), 437, doi: 10.1007/s10661-017-6119-8
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is a remote sensing technology that uses light in the form of pulses to measure the range between a sensor and the Earth’s surface. Recent increase in availability of
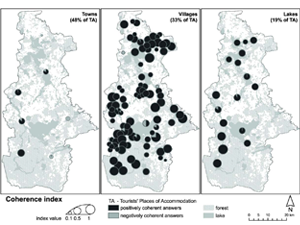
Derek M., Woźniak E., Kulczyk S. (2017) Tourism in a nature-based destination: the human versus the ecological perspectives, Tourism Geographies, 10.1080/14616688.2017.1314545
In the tourism studies literature, wilderness has been addressed from two perspectives. From the first, human, perspective wilderness is a social, subjective construction that exists only in the mind of its users. From the
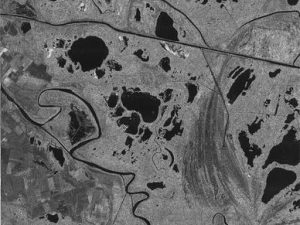
Malinowski, R., Groom, G.B., Heckrath, G. (2017) Do Remote Sensing Mapping Practices Adequately Address Localized Flooding? A Critical Overview, et al. Springer Science Reviews, doi: 10.1007/s40362-017-0043-8
Local-scale flooding (LSF) is usually characterized by much less severe damage compared to extreme flood events; however, it does have marked local environmental influence, especially when it is characterized by regular and frequent occurrence
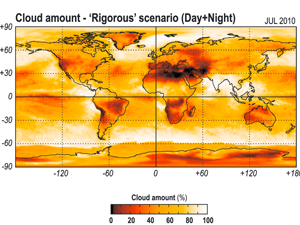
Kotarba, A.Z. (2015) Impact of Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) cloud mask interpretation on cloud amount estimation, Journal of Geophysical Research, Volume 120, Issue 17, September 2015 Pages 8971–8986, doi: 10.1002/2015JD023277
Cloud masks serve as a basis for estimates of cloud amount, which is an essential parameter for studying the Earth’s radiation budget. The most commonly used cloud mask is a simple thematic classification, which
 Wersja polska
Wersja polska English version
English version